Global Environment Facility
Overview of the Global Environment Facility (GEF)
Background
The Global Environment Facility (GEF) was established on the eve of the 1992 Rio Earth Summit to help tackle our planet's most pressing environmental problems.
The GEF serves as a "financial mechanism" for five conventions:
- Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD)
- United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC)
- Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs)
- UN Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD)
- Minamata Convention on Mercury
Objective
To provide funding to developing countries and countries with economies in transition to meet the objectives of the international environmental conventions and agreements
Fund to support adaptation to climate change under the GEF's control and operation
- Three funds related to climate change adaptation exist under the GEF's control and operation.
| Fund | Summary |
|---|---|
| The Global Environment Facility (GEF) Trust Fund | The GEF trust fund provides funding to developing countries and countries with economies in transition to meet the objectives of the international environmental conventions and agreements. |
| Special Climate Change Fund (SCCF) | SCCF was established under the UNFCCC in 2001. Currently, it provides funding to Non-Annex I countries for climate change adaptation and technology transfer. |
| Least Developed Countries Fund (LDCF) | LDCF was established under the UNFCCC in 2001. It provides funding to LDCs for the preparation and implementation of National Adaptation Programme of Action (NAPA). |
Overview of GEF Funding
This section details three funds under the GEF.
(1) GEF Trust Fund
① Objective
To support developing countries and countries with economies in transition to meet the objectives of international environmental conventions and agreements
② Eligible Applicants
Countries may be eligible for GEF funding in one of two ways:
- if the country has ratified the conventions the GEF serves and conforms with the eligibility criteria decided by the Conference of the Parties of each convention; or
- if the country is eligible to receive World Bank (IBRD and/or IDA) financing or is an eligible recipient of UNDP technical assistance through its target for resource assignments from the core (specifically TRAC-1 and/or TRAC-2).
③ Areas of Support
To achieve the objectives of multilateral environmental agreements, it is required that the GEF support country priorities that ultimately aim to tackle the drivers of environmental degradation in an integrated manner.
Therefore, the Areas of Support are as follows:
Biodiversity, Chemicals and Waste, Climate Change Mitigation, Climate Change Adaptation, International Waters, Land Degradation, Sustainable Forest Management
④ Type of Funding
Grant including technical support, investment in infrastructure, planning, and the preparation of reports required by multilateral environmental agreements
⑤ Type and Size of Support
- Full-sized Project (FSP): GEF Project Financing of more than USD 2 million.
- Medium-sized Project (MSP): GEF Project Financing of less than or equivalent to USD 2 million.
- Enabling Activity (EA): A project for the preparation of a plan, strategy, or report to fulfill commitments under a Convention.
- Program: A longer-term and strategic arrangement of individual but interlinked projects that aim to achieve large-scale impacts on the global environment.
⑥ Eligibility Criteria
| No. | Eligibility Criteria |
|---|---|
| 1. | National priority: The project must be driven by the country (rather than by an external partner) and be consistent with national priorities that support sustainable development. |
| 2. | GEF priorities: The project has to address one or more of the GEF focal area strategies (Biodiversity, International Waters, Land Degradation, Chemicals and Waste, and Climate Change Mitigation, as well as cross-cutting issues like sustainable forest management). |
| 3. | Financing: The project has to seek GEF financing only for the agreed incremental costs on measures to achieve global environmental benefits. |
| 4. | Participation: The project must involve the public in project design and implementation, following the Policy on Public Involvement in GEF-Financed Projects and the respective guidelines. |
(2) Special Climate Change Fund (SCCF)
① Objective
To support adaptation and technology transfer projects/programs in all developing country parties to the UNFCCC that:
- are country-driven, cost-effective, and integrated into national sustainable development and poverty-reduction strategies; and
- consider national communications or NAPAs and other relevant studies and information provided by the Party.
② Eligible Applicants
Organizations in developing countries (governmental organizations, non-governmental organizations, community-based organizations (CBO))
③ Areas of Support
- Adaptation
Water Resources Management, Land Management, Agriculture, Health, Infrastructure Development, Fragile Ecosystems (including mountain ecosystems), Integrated Coastal Zone Management, and Climatic Disaster Risk Management - Transfer of Technology
Environmentally sustainable technologies focusing on but not limited to technologies to reduce emissions or atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases, aligned with the recommendations of the national communications, technology assessments (TNAs), and other relevant information
④ Type of Funding
- Grant
⑤ Type and Size of Support
- Full-sized Projects (FSP): Projects of more than USD 1 million
- Medium-sized Projects (MSP): Projects of USD 1 million or less
⑥ Eligibility Criteria
| No. | Approval Criteria |
|---|---|
| 1. | Basic project idea (adaptation benefit and additional cost argument for adaptation projects)
|
| 2. |
Fit with country priorities
|
| 3. |
Implementation setup
|
| 4. |
Indicative budget and co-financing
|
(3) Least Developed Countries Fund (LDCF)
① Objective
The NAPA process including preparation and implementation has two main objectives:
- Identifying adaptation priorities at the national level for LDCs
- Expedited access to funds for LDCs to address the most urgent and immediate needs
② Eligible Applicants
Organizations in LDCs (governmental organizations、non-governmental organizations, CBOs)
③ Areas of Support
Climate change adaptation
④ Type of Funding
Grant
⑤ Type and Size of support
- Full-sized Projects (FSP): Projects more than USD 2 million
- Medium-sized Projects (MSP): Projects of USD 2 million or less
⑥ Eligibility Criteria
| No. | Approval Criteria |
|---|---|
| 1. |
Basic project idea (adaptation benefit and additional cost argument)
|
| 2. |
Fit with NAPA priorities
|
| 3. |
Implementation setup
|
| 4. |
Indicative budget and co-financing
|
| No. | Approval Criteria |
|---|---|
| 1. |
Project idea and additional cost argument
|
| 2. |
Implementation setup
|
| 3. |
Indicative budget and co-financing
|
| 4. |
Letters of endorsement for all co-financing (Co-financing is clarified in the next section.) |
| 5. |
Monitoring and Evaluation Framework
|
Apply for GEF Funding
The diagram below shows the application flow for the three funds mentioned above.
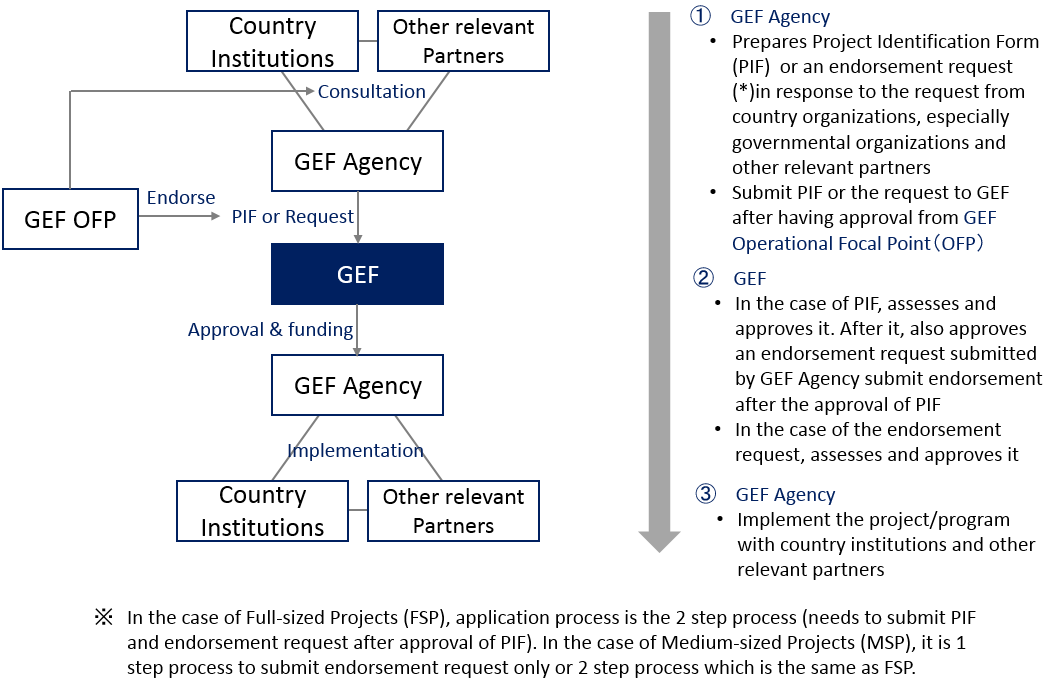
| Organization | Summary | |
|---|---|---|
| ① | GEF Agency |
|
| Country Institutions |
|
|
| Other relevant Partners |
|
|
| GEF Operational Focal Point (OFP) |
|
|
| ② | GEF |
|
Forms
Application forms are according to the size/scheme of the project such as FSPs and MSPs.
Project List
Reference
- GEF Project and Program Cycle Policy
- Accessing Resources under the Special Climate Change Fund (SCCF)
- Accessing Resources under the Least Developed Countries Fund (LDCF)