
Why engage in Adaptation Planning?
With the deepening climate crisis, there is growing awareness of the urgent need for climate change adaptation. The impacts of climate change are diverse and vary from one country to another. Therefore, national governments, local governments, companies, and local communities need to look at this issue from a medium to long-term perspective and take adaptation measures according to their own circumstances. The Adaptation Plan Development Process, implemented both in developing and developed countries, from central to local governments and non-state actors, is integral to tackle this challenge.
Adaptation Plan Development Process
In general, the Adaptation Plan Development Process is an iterative process of four steps:
- Assessment of climate change risks
- Planning for adaptation
- Implementation of adaptation measures
- Monitoring and evaluation
It also calls for institutional arrangements, such as a national climate change committee, that support and promote the effective implementation of this process. This process enables adaptation measures to be continually improved, and ensures flexible and adaptive management of adaptation. This approach also considers the changing climate as well as social, economic, and environmental conditions over time.
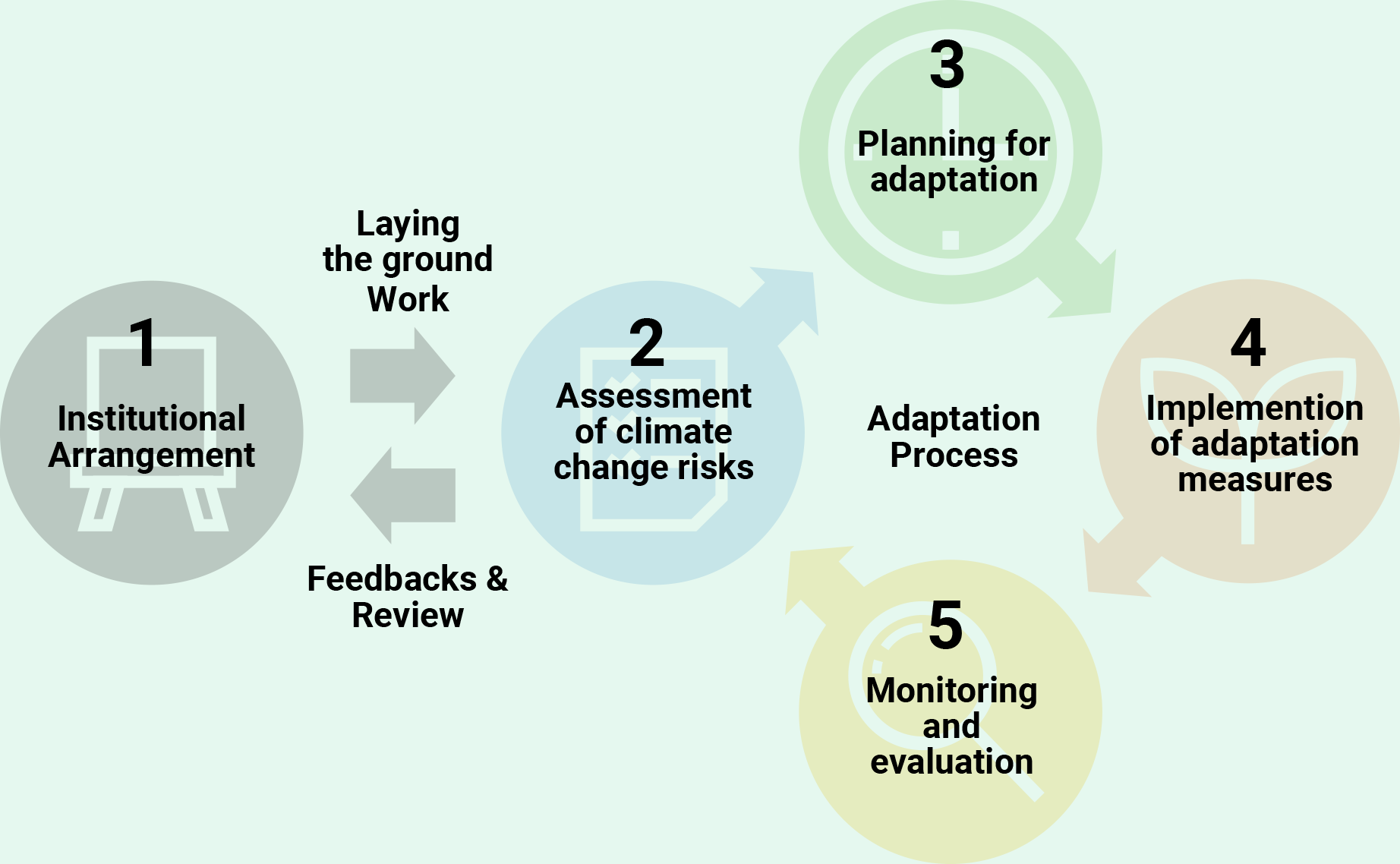
- Institutional Arrangement
-
The process starts by establishing institutional arrangements for designing and developing adaptation plans. This could involve , for example, a climate change committee, or a branch of the relevant ministry, depending on the situation in the particular country or region. A coordination mechanism also needs to be considered, such as a council to bring together different ministries relevant to adaptation. It is important to note that these institutional arrangements need to be revisited and reviewed periodically, and refined as appropriate. Finally, it is also vital to develop the capacity needed to plan and implement adaptation measures. Revisions to institutional arrangements and capacity may then become part of the adaptation plan.
- Assessment of climate change risks
-
The substantive adaptation process begins by assessing climate change risks. Risk assessment normally has three elements:
- Assessing climate change impacts based upon climate change scenarios
- Assessing vulnerability
- Assessing exposure
The main objective of this step is to identify and prioritize climate change risks facing the region/sector. In the assessment, community-based approaches should be incorporated to collect local experiences and knowledge. Such an approach is particularly useful when scientific data are not available in certain contexts.
- Planning for adaptation
-
Based on the identified climate change risks, adaptation measures need to be developed and put together in line with the adaptation plan. The plan outlines the necessary adaptation measures in a systematic and comprehensive manner, involving a review and stock-taking of existing policy measures that can be considered as part of adaptation. In planning adaptation measures, it is crucial to prioritize adaptation measures with certain criteria, such as the urgency and severity of the risks. If there are risks that are not currently significant but are expected to be significant in the future, the plan should include necessary preparatory measures so that the countermeasures are ready once such risks are realized. To the extent possible, the necessary budget calculations and funding sources should be discussed. The plan should also touch upon fundamental elements such as arrangement for implementation, M&E process, and plans to promote research to fill knowledge gaps.
- Implementation of the adaptation plan
-
Once the adaptation plan has been developed, the next step is to implement it. Mobilizing the plan for implementation requires certain arrangements such as the authorization and then coordination with relevant actors. Effective collaboration with relevant ministries, local governments, businesses, and civil society is essential for effective adaptation. Whenever appropriate, actions should be taken to integrate adaptation measures into various national plans, such as development or environmental protection plans. In addition, if funds for the implementation of adaptation measures are inadequate, additional funding opportunities should be explored.
- Monitoring and evaluation
-
Finally, implementation of the adaptation plan should be monitored and evaluated. M&E is useful for understanding the status of the adaptation plan, verifying its effectiveness, and identifying any gaps. The results of M&E need to be reflected in the revised adaptation plan and subsequent implementation processes. M&E is an essential element to ensure that the adaptation plan is verified, updated, and adaptively managed according to any changes in circumstances.
Reference:
UNFCCC, What do adaptation to climate change and climate resilience mean?
Least Developed Countries Expert Group. 2012. National Adaptation Plans. Technical guidelines for the national adaptation plan process. Bonn: UNFCCC secretariat. Bonn, Germany. December 2012.

- NAP PROCESS UNDER THE UN FRAMEWORK
- Understand why adaptation planning is necessary in the long run to implement the Paris Agreement. Learn about the latest trends in international adaptation negotiations and support systems for NAP formulation under the UN bodies.

- STATUS OF ADAPTATION IN THE ASIA-PACIFIC
- What adaptation plans are being developed in the Asia-Pacific? Learn some of the most distinctive features and best practices, and find the latest information on adaptation plans being carried out by your neighboring countries or countries facing similar challenges.

- Finance & Implementation
- Identify key points, good practices, and useful examples for financing both in the planning and implementation phases of adaptation.

- Monitoring & Evaluation
- Once adaptation measures are implemented, Monitoring and Evaluation (M&E) is conducted to track and evaluate the effectiveness of adaptation measures. Find useful resources including the latest discussions and good practices here.
