Wetlands as an NbS for water purification
- Sugadaira, Nagano, Japan

ABOUT THIS ISSUE
Intense agricultural activities cause surface water pollution in Sugadaira, Nagano Prefecture, Japan
SOLUTION
Research based evaluation of a wetland as an NbS for water purification
Wetlands and their vital importance as an NbS for water purification: A case study from Sugadaira, Nagano, Japan
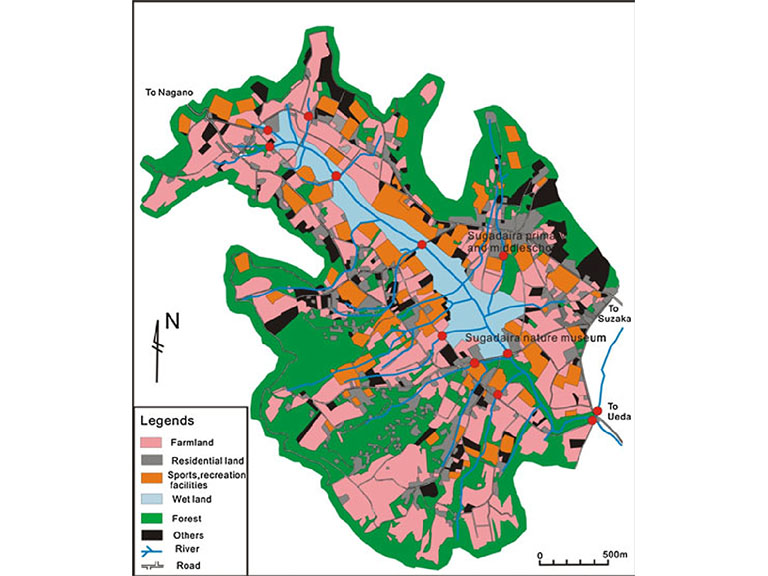
Sugadaira is a village located in central Nagano Prefecture, Japan, that has an altitude of about 1,300 m above mean sea level and a cold climate with an average annual temperature of 6.5°C and snow cover from December to March. It is a popular ski and snowboard resort with a wide range of courses, regular powder snow conditions, and spectacular views of the surrounding regions. It is also very famous for hosting various sports camps and matches for soccer, mini golf, rugby, etc. In addition, agriculture is one of the main sources of livelihood for local people, so this area experiences intensive farming. A land use and land cover map is shown in Figure 1. Due to the excessive use of fertilizers, the quality of surface water bodies in Sugadaira have worsened in the last few years, especially in terms of nitrate concentrations. If the human body is exposed to high nitrate concentrations over a long period of time, it may cause various health issues, such as methemoglobinemia and blue baby syndrome.
Importance of NbS
Water quality deterioration is an important global environmental issue, and water treatment or purification using only man-made infrastructure is not a sustainable long-term solution. Most often this infrastructure is resource intensive (both in terms of money, land, and people) and may not be suitable for all locations. The management of such infrastructure also requires highly skilled people. Considering these shortcomings, decision makers are looking for alternate solutions i.e., NbS. For water quality improvement, various NbS are available, including the use of wetlands and vegetation such as water hyacinth.
Use of wetlands as an NbS for water quality improvement
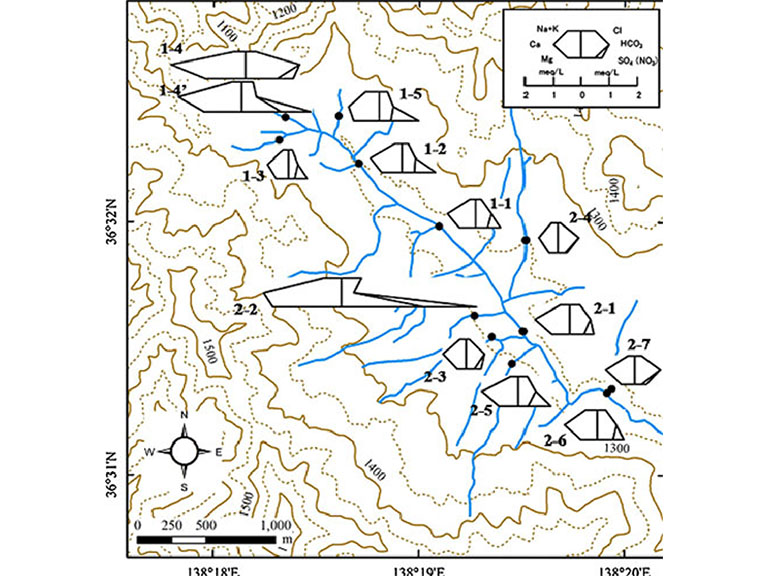
Here, this research work showcasing the efficiency of wetlands for water quality improvement is summarized. Water samples were collected from in and around Sugadaira Wetland and various water quality parameters were analyzed. A very interesting pattern of nitrate concentration was observed, even within a small area (Figure 2). In Figure 2, the standard sample is shown in the legend and the concentration of nitrate is indicated by the line that extends from the bottom right corner of each plot. Water samples 1-4’, 2-2, and 2-5 had a relatively higher concentration of nitrate. To further investigate the main factor causing this water pollution, land use and land cover map was superimposed over the water quality distribution map. It was evident that the points that had high concentrations of nitrate were mostly from the left side of the mainstream in areas where agricultural activities and other processes like microbial mineralization are more extensive. Points lying on the right side of the mainstream or near the wetland had low concentrations of nitrate, indicative of anaerobic conditions in the wetland that enhance denitrification. Here, denitrification means changing the toxic nitrate compound into other less toxic compounds.
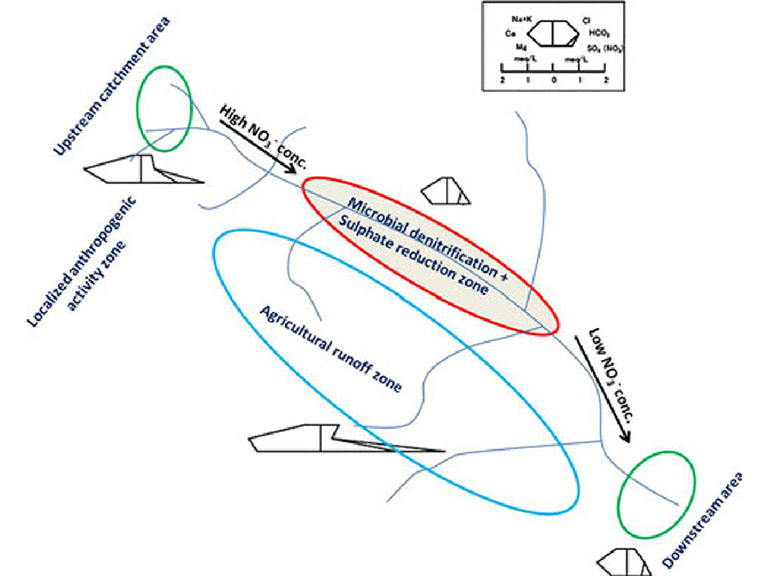
To show this whole process in a more simplistic way, a schematic diagram is presented in Figure 3. The processes influencing water quality in Sugadaira are localized nitrate enrichment from agricultural runoff, domestic sewage from an upstream watershed area, sulphate reduction and denitrification along the wetland area, and freshening phenomena in the downstream region.
This case study clearly shows the positive effect of wetlands on water quality improvement and hence the possibility to use wetlands as a part of an NbS should be further explored, especially in places with limited monetary resources.
Location
References
-
Kumar, P., Iwagami, S., Yaping, L., Mikita, M., Tanaka, T., & Yamanaka, T. (2011) Multivariate approach for surface water quality mapping with special reference to nitrate enrichment in Sugadaira, Nagano Prefecture (Japan). Environment Systems and Decisions, 31: 358-363.
Discover More

Rice fields as natural infrastructure for groundwater recharge
- Kumamoto, Japan

Mangroves reduced damage to earthen embankment
- Sundarban, India

Floating communities’ adaptation to environmental changes
- Tonle Sap Lake, Cambodia

Miyawaki urban forests to fight climate change and pollution issues
- Delhi, India

